Hardware, which includes screws, bolts, nuts and other fasteners, is an essential component in many industries, from construction to mechanical engineering. To ensure quality, safety and interchangeability, these products follow well-defined standards, such as DIN, ISO and EN. In this article we will explore the main standards applied to fasteners and why they are critical.

Header of DIN EN ISO 4014
What Are Hardware Standards?
Hardware standards are technical regulations that define product characteristics, such as:
- Dimensions and tolerances: length, diameter, thread.
- Materials: steel, stainless steel, special alloys.
- Mechanical properties: tensile strength, hardness.
- Surfaces and treatments: galvanizing, anti-corrosion coatings.
The best-known standards are:
- DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung): German standard, among the first to be adopted.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): International standard, used worldwide.
- EN (European Norm): Harmonized European standards.

Classification of Screws: Examples of Standards
Each type of screw or bolt is described in detail in a specific standard. For example:
- DIN EN ISO 4014: Hexagon head screws with threaded shank.
- DIN EN ISO 4032: Type 1 hexagonal nuts.
- ISO 10642: Hex socket countersunk head cap screws.
These standards ensure that a screw produced in one country can be used in another without compatibility problems.
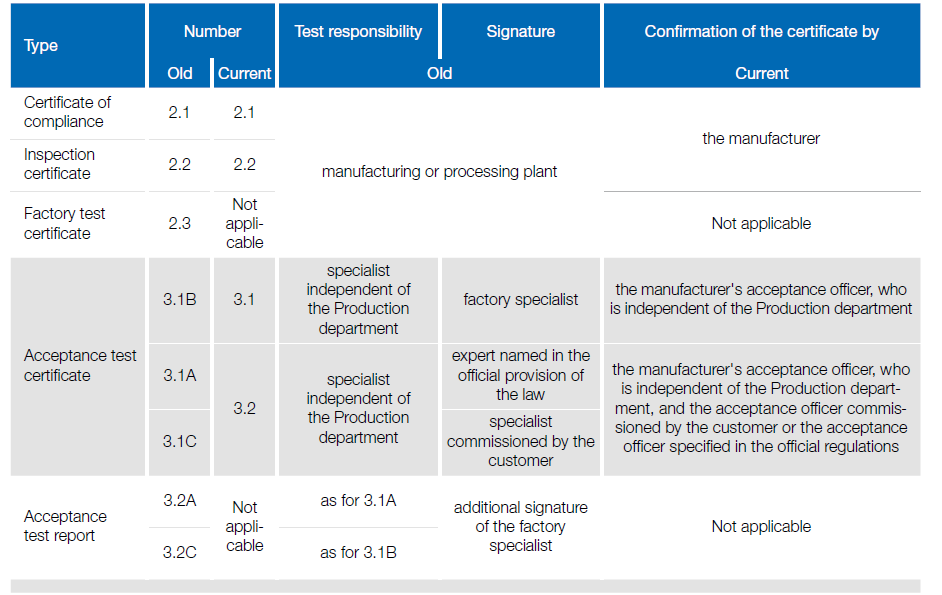
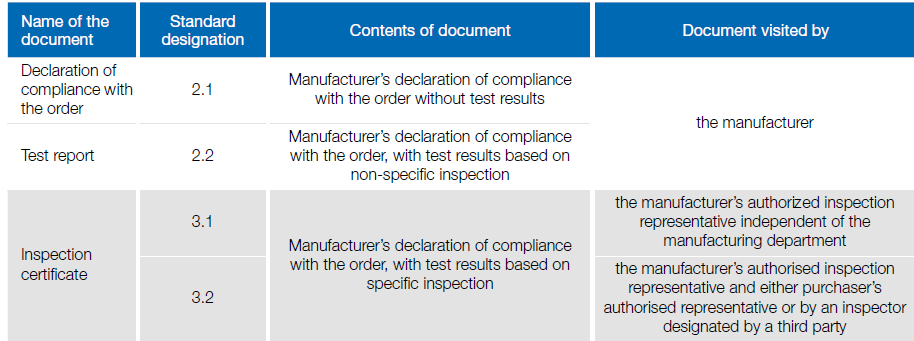
Test certificates according to ISO 10474:2013-07
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Safety
The standards define the mechanical properties of fasteners to ensure that they can withstand the expected stresses. A common example is the strength class given for steel bolts, such as 8.8 or 10.9, according to DIN EN ISO 898-1:
- The first number indicates the minimum tensile strength (800 N/mm² for 8.8).
- The second number represents the elastic limit (80% of the tensile strength for 8.8).
Stainless Steel: Standards and Applications.
For applications in corrosive environments, such as the food or marine industries, stainless steel screws are used. The most common classes are defined by DIN EN ISO 3506:
- A2: Corrosion resistant in standard environments.
- A4: Resistant in highly corrosive environments, such as marine.
Each stainless steel screw is accompanied by a strength class (e.g., 70, 80), which represents the minimum tensile strength in N/mm².
Certifications and Documentation
To ensure quality and traceability, fasteners are often accompanied by certificates according to DIN EN 10204:
- Certificate 2.1: Generic Declaration of Conformity.
- Certificate 3.1: Specific tests approved by an independent expert.
- Certificate 3.2: Tests approved by a customer representative and an external expert.
These documents are critical for regulated industries, such as automotive and aerospace.
Why Are Standards Important?
Following standards in manufacturing and purchasing screws and bolts offers several benefits:
- Interchangeability: Standardized components can be used in different systems.
- Quality: Product properties are guaranteed.
- Regulatory compliance: Standards help comply with laws and regulations.
- Safety: Products are designed to withstand the expected stresses.
Conclusion
Hardware standards are essential to ensure compatibility, safety and quality in every industry.
When choosing screws, bolts or nuts, always check that they comply with the latest standards, such as DIN, ISO or EN.
This way, you can count on reliable products that comply with international standards.
Need technical support or a specific product?
Credits: Bollhoff GmbH


































